Individuals were rated as more attractive when they were observed in a group rather than alone, reported University of California, San Diego’s Drew Walker and Edward Vul.
Individuals are generally perceived as similar but not identical to the average group face.
This group average is seen as more attractive than group members’ individual faces, thanks to a perceptual bias called the ”cheerleader effect.”
People who are judged attractive are also ascribed positive characteristics including good health, good genes, intelligence, and success as a result of attribution bias.
There is consensus across cultures and genders on ratings of physical attractiveness, found University of Louisville’s Michael R. Cunningham, Anita P. Barbee and Perri B. Druen, who collaborated with Alan R. Roberts of Indiana University and Chung Yuan Christian University’s Cheng-Huan Wu.
Features rated as most attractive for women include:
- High cheekbones and forehead,
- Fuller lips,
- Large, clear eyes,
- Shorter jaw,
- Narrower chin,
- Waist-to-hips ratio of 7:10,
- Body Mass Index (BMI) of 20.85.
Women’s weight was not as significantly related to attractiveness as the elements above.
Preferred characteristics for men were:
- Large jaw and brow,
- Prominent cheekbones,
- Broad chin,
- Waist-to-hips ratio of 9:10,
- About 12 percent body fat.
Smooth skin, shiny hair, and facial symmetry were rated as attractive for both women and men.
Individuals’ physical attractiveness focuses observers’ attention, and enables assessments of personality traits based on brief interactions, according to University of British Columbia’s Genevieve Lorenzo and Jeremy Biesanz with Lauren Human of University of California, San Francisco.
Observers more accurately identified personality traits of physically attractive people.
These ratings were more similar to attractive people’s self-reported personality traits.
Volunteers showed a positive bias toward attractive people and accurately identified the relative ordering of attractive participants’ Big Five personality traits (extraversion, conscientiousness, agreeableness, openness to experience, and emotional stability, also called “neuroticism”).
Raters also accurately evaluated CEOs’ competence, dominance, likeability, maturity, and trustworthiness by viewing photographs of the executives’ faces in a study by University of Toronto’s Nicholas Rule and Nalini Ambady, then of Tufts.
Thirty volunteers assessed CEOs’ “leadership success” based on appearance alone, and these rating were significantly related to profitability of the organizations the CEOs led.
CEOs and non-executives compete in an unconscious “corporate beauty contest,” asserted John Graham, Campbell Harvey and Manju Puri of Duke.
Executives who were viewed as attractive are assigned positive attributions, according to these researchers.
Photos of more than 100 white male chief executive officers of large and small companies were paired with with photos of non-executives with similar facial features, hairstyles and clothing.
Nearly 2,000 participants assessed photos and rated CEOs as competent and attractive more frequently than non-executives.
However, volunteers were less likely to rate CEOs as likeable and trustworthy.
Those rated as “competent” earned more money, but in this study, CEO appearance wasn’t associated with company profitability.
Specific facial structures, not just attributed personality traits, were associated with superior business results, according to University of Wisconsin’s Elaine Wong and Michael P. Haselhuhn working with Margaret E. Ormiston of London Business School.
Firms that achieved superior financial results tended to have male CEOs with wider faces relative to facial height, particularly among organizations with “cognitively simple leadership teams.”
Evolutionary biology suggests that specific facial structures may be perceived as associated with trustworthy leadership skills, leading to attributions of competence, and inspiring loyalty to follow.
-*What positive bias do you observe toward attractive individuals in the workplace?
-*How do you harness the positive bias toward attractive individuals?
RELATED POSTS:
- How Accurate are Personality Judgments Based on Physical Appearance?
- “Self-Packaging” as Personal Brand: Implicit Requirements for Personal Appearance?
- Executive Presence: “Gravitas”, Communication…and Appearance?
- How Much Does Appearance Matter?
©Kathryn Welds






















































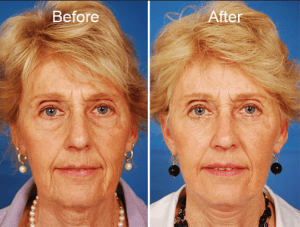 Raters assigned higher scores for likeability, social skills, and attractiveness to the images following plastic surgery compared with pre-surgery image ratings.
Raters assigned higher scores for likeability, social skills, and attractiveness to the images following plastic surgery compared with pre-surgery image ratings.












