People are motivated by goals that enable:
- Relatedness to others,
- Competence in skillful performance,
- Autonomy in directing effort, according to Columbia’s Heidi Grant Halvorson.

Heidi Grant Halvorson

Juliana Breines
- She advocated working toward “better” performance rather than focusing on achieving the goal.
This can be accomplished by acknowledging mistakes and practicing self-compassion, suggested by Berkeley’s Juliana Breines and Serena Chen, and University of Texas‘s Kristin Neff.
The Relatedness-Competence-Autonomy model aligns with Daniel Pink’s suggestion that meaningful goals enable two similar features and one different element:

Daniel Pink
- Autonomy (same): Controlling work content and context,
- Mastery (like Competence): Improving skill over time through persistence, effort, corrective feedback,
- Purpose (in contrast to Relatedness): Being part of an inspiring goal.
Halvorson suggested ways to move closer toward goals:

Serena Chen
-Consider the larger context of specific productive actions,
-Define reasons for doing what needs to be done – the “why,”
-Use “implementation intentions” to prepare responses for challenging situations:
–If “x” occurs (specify time, place, circumstance),
-Then I will respond by doing, thinking, saying “y.”
-
- “When I feel anxious, I will focus on inhaling and exhaling slowly for 60 seconds.”
- “When it’s 7 am, I will walk for 10 minutes,”

Kristin Neff
-Apply implementation intention routines (habits) for “strategic automation” to reduce decision-overload that may undermine self-control,
-Focus on something interesting for five minutes to evoke positive feelings,
-Review “small wins” and progress toward goals.
Goal persistence can be increased, reported Stanford’s Teresa Amabile and Steven Kramer in a study of employees at seven companies.

Teresa Amabile
They found that “catalysts” and “nourishers” continue movement toward goals:
-
- Capitalise on preferred motivational style:
-“Promotion-focused” (maximise gains, avoid missed opportunities, powered by optimism),
-“Prevention-focused” (minimise losses, variance, powered by cautious pessimism),
- Build willpower by committing to one specific, positively-stated behavior change (“walking for 10 minutes a day every day”)
- Apply “implementation intentions,”
- Focus on a limited number of achievable goals,
- Enlist “mental contrasting” to think about the satisfaction of achieving the goal.
- Capitalise on preferred motivational style:

Carol Dweck
Halvorson collaborated with Stanford’s Carol Dweck and quoted Henry Ford: “Whether you think you can or think you can’t, you’re probably right” to underscore the value of optimistic engagement with goals.

Henry Ford
They synthesized Dweck’s work on “mindsets” with Halvorson’s recommendations for setting, monitoring, protecting, executing, and celebrating goals.
An earlier post outlined Dweck’s definitions of mindsets:
• Fixed Mindset: Belief that personal capabilities are given, fixed, limited to present capacities, associated with fear, anxiety,
• Growth Mindset: View that personal capabilities can expand based on commitment, effort, practice, instruction, correcting mistakes, collaboration.

Peter Gollwitzer
Columbia’s Peter Gollwitzer refined “mindsets” by distinguishing the Deliberative Mindset of evaluating which goals to pursue from the Implementation Mindset of planning goal execution.
His team found that the Deliberative Mindset is associated with:
-
- Accurate, impartial analysis of goal feasibility and desirability,
- Open-mindedness.
In contrast, the Implementation Mindset is linked to:
-
- Optimistic, partial analysis of goal feasibility and desirability,
- Closed-mindedness.
Halvorson, Dweck and Gollwitzer translated their research on self-determination and motivation into practical recommendations for goal seekers:
-
- Adopt a supportive “mindset,”
- Practice “self-compassion” when encountering setbacks to achieving goals,
- Design effective responses to anticipated challenging situations,
- Use “implementation intentions” and “strategic automation” toward goals,
- Consider incremental progress toward goals.
-*What approaches help you work toward goals?
Related Posts:
- Hacking Human Behavior: “Tiny Habits” Start, Maintain Changes
- Two Approaches to Following-Through on Plans, Adapting to Changes
- Career Navigation by Embracing Uncertainty
- Creating Productive Thought Patterns through “Thought Self-Leadership”
- Action Beats Visualization to Improve Performance
©Kathryn Welds












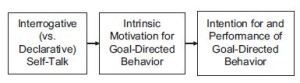



































 Pink’s later book,
Pink’s later book, 



