People often make “affective predictions” about choice of life partner, occupation, residence, yet most everyone makes small, but systematic errors in forecasting personal emotional responses.
These misjudgments can negatively affect personal health, happiness, financial well-being, and interpersonal relationships.
University of British Columbia’s Kostadin Kushlev and Elizabeth Dunn identified these decision biases, and noted that one of the most well-known and widely-occurring affective forecasting errors is impact bias, the tendency to overestimate the intensity of emotional responses to future positive and negative events.
In addition, Kushlev and Dunn reported that people tend to overestimate the duration of future emotional reactions, labeled durability bias.
Durability bias (focalism) can occur when people rely on the “rational system” for information processing, according to Seymour Epstein of University of Massachusetts.
His Cognitive-Experiential Self Theory proposes that the “rational system” is used to make affective forecasts using slow, analytic and abstract processing.
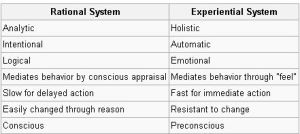 In contrast, the “experiential system” of information processing is rapid, associative, holistic, and concrete.
In contrast, the “experiential system” of information processing is rapid, associative, holistic, and concrete.
Shifts between rational (“cold”) and experiential (“hot”) decision systems can cause another bias, “Empathy gap.”
Epstein posits that rational system processing can lead to imagining the event isolated from its broader context, which can underestimate its emotional impact.
This can lead to focus on and overvalue distinctive, observable characteristics.
Immune neglect is a related error, when people underestimate their likelihood of later reinterpreting future events to reduce regret.
Underestimating the power of future physical states is another predictive error recognised in Alcoholics Anonymous guidance to analyse whether cravings occur when people experience “HALT” (“Hungry, Angry, Lonely, Tired”.)
“Personality neglect,” is another error that occurs when people underestimate the influence of personal dispositions and characteristics.
Expectations affect future emotions, according to Wilfrid Laurier University’s Roger Buehler, Vassili Spyropoulos and Kent C. H. Lam with Cathy McFarland of Simon Fraser University. They found that those with positive expectations experience more positive present and future emotions. This optimism bias may provide protection and benefit to each individual’s “psychological immune system.”

Kristin Weger
People can reduce errors in predicting future emotions by evaluating expectations in comparison to actual experience during a “post-mortem” session to review “lessons learned,” found University of Alabama at Huntsville’s Kristin Weger and Sandra Carpenter.
-*How accurate are you in predicting your feelings about a specific choice or situation in the future?
-*How do you detect and mitigate bias in predicting your future emotional reactions?
-*What positive and negative impacts have you observed in affective forecasting errors?
RELATED POSTS:
- Useful Fiction: Optimism Bias of Positive Illusions
- Overcoming Decision Bias: Allure of “Availability Heuristic”, “Primacy Effect”
- Biases in Unconscious Automatic Mental Processing, and “Work-Arounds”
- Detect and Mitigate Decision Biases
- Human Decision Biases Modeled with Automatons
- Hypothetical Questions May Lead to Bias
- Minimize “Quest for the Best” Bias
- Reduce Evaluator Bias: Showcase Best Features in Any Offer
- Decision Maximizers, Satisficers and Potential Bias
- Creating Productive Thought Patterns through “Thought Self-Leadership”
©Kathryn Welds







 He argues that contemporary world economic conditions require six conceptual, subjective, holistic “senses” to transform abundant information into meaningful and actionable implications:
He argues that contemporary world economic conditions require six conceptual, subjective, holistic “senses” to transform abundant information into meaningful and actionable implications:



